Post-Day-2-Paper-currency
Day 2
Dated 2/5/2020;
Topic :: Paper and electronic currency
Yesterday we discussed the evolution of money from barter system to coins. Today we seek to explore the functioning of paper money or Legal Tender.
Term for today
Fiduciary money: Fiduciary money refers to money backed up by trust between the payer and payee
Types
- Non Legal Tender ->like cheque, Demand draft, etc. in this type a person can refuse to accept the payment in India and can ask for alternatives like cash.
- Legal Tender-> this contains coins and currency notes.
The legal tender of a currency is further of two types
- Limited Legal Tender:: under coinage act states that it (coins) can be use to settle a limited amount of debt like anyone can legally reject a payment in 50p for amount above Rs 10. And same goes for other coin denominations with limit of 1000rs.
- Unlimited legal Tender::Under RBI act 1934 Every note is unlimited legal tender but with reasonable restriction of rs 3L after denomination
Fiat currency:: currency notes form a system if fiat currency where binding to the command of government a currency can settle debt which no one can refuse.
The issuance of Indian Fiat Currency 1.Coinage act 1906 Government can issue the following denominations
- All coins up to value of 1k
- Rs 1 note (ever noticed Rs 1 note is signed by finance secretary not by RBI governor)

- RBI act 1934:: from rupees 2 to 10000 all notes can be issued by RBI signed by the Governor OF RBI
Any currency note issued by any government should be supported by a physical asset underneath in the government reserves. Have you ever read the clause on a currency note? I promise to pay the bearer the sum of ____rupees
Signed by Governor of RBI

This clause grantees that the person with the note can approach any RBI branch to prove the value of note. Though the fact is ignored by everyone of us but this clause is the main reason behind the value of a piece of paper.
Earlier the physical asset used was GOLD..yes RBI had permission to print currency notes against the Gold reserves, and you could legally approach the RBI governor to get the underlying gold in exchange of your owned currency note.
But now we have shifted to Minimum Foreign reserve system
Here instead of Gold the INR is backed by securities (investments) in foreign reserves.
Bank Money and Digital Transactions
Cheque :: it is a legally binding non fiat type of medium of exchange of money. There can be three types of non fiat money.
- Simple bank cheque: 3Parties : We all are familiar with this type
-
A Bill of Exchange:: it is a legal agreement stating that is there are three persons say Bholla, Laddu and Babla, say Bholla Singh has to give Laddu a sum of 10K but he does not have money and Laddu needs money immediately, so Bholla goes to Babla and says that is Babla can pay laddu on a bill of exchange means babla will clear the amount of laddu for bholla singh but will receive money after sometime when bholla arranges, This bill of exchange is written on a legal paper with Revenue stamps.
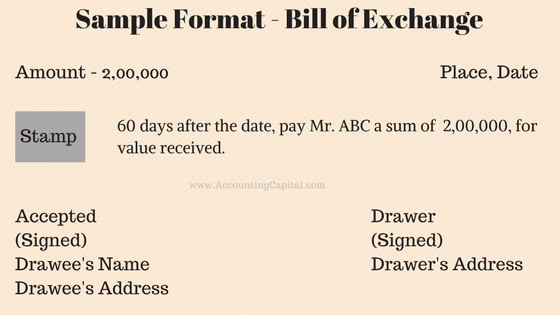
- Promissory note:: It is a signed document containing a written promise to pay a stated sum to a specified person or the bearer at a specified date or on demand
Types of Cheques Classification
- Based on date :
- stale dated ::expired cheque, The one which has passed 3 Months from the date of issue.
- Post dated :: cheque bearing a future date of issue.
- Ante dated:: Cheque issued before the date of contract or deal.
- Based on Crossing::
- Open cheque :: the check with no crossing is an open cheque and can be cashed for bearer. This poses risk of exploitation on loss of cheque.
- General Crossing :: A cheque having two parallel lines made on top left corner represents that the cheque can be paid only into a bank account of the person with name on it.
Now how do you request your bank to process a cheque in your account? Once you reach you bank, Write your account number and phone number on backside of the cheque you’ve got. And drop it into a box kept at bank named as cheque drop box. Bank routinely takes out cheques from that box and process those under the CTS 2010 (cheque truncation system) earlier cheques were manually posted to the issuing branch to verify signatures and it’s authenticity, This took a lot of time and was bulky work.

Now under CTS a scanned copy of cheque is generated using MICR (magnetic Ink Character recognition) and OCR (optical character recognition). This has made single day cheque clearance possible. Lets see the parts of a cheque to get a practical feel There is a 11 digit IFSC code this is unique for each branch (Indian Financial System Code) A 9 Digit MICR code printed with magnetic ink for CTS procedure The Picture shows a cancelled cheque that is sometimes used to share account details with someone like your mutual fund Broker or an Investment manager. Cheque is also printed on high security leaflets costing around 2.5 rupees a leaflet, but believe me I’ve received a cheque of 25p from a clearance . And yes I can unmask my account number if someone wants to pay? #pun intended . Bouncing of a Cheque:: when the person issuing a cheque has insufficient funds the cheque can not be cleared hence is referred to as a bounced cheque. This is legally punishable and a offence under the IPC. To avoid bouncing and messed up payments several companies ask and prefer payments by DD or Demand Draft it is a similar instrument as a cheque but in this the amount is deducted first before issuing and bank also levies a reasonable charge for generating it.
Hope this helps.
It’s just an effort
Anubhav Gupta
If any query or doubt call @ 7889187722